Class NodeLink2 Extends GraphModifier
Connects two nodes via two intermediate point nodes.
In contrast to the NodeLink component, this link type will not connect the nodes directly instead it will create two point nodes at the start and end position of this link and connect through those nodes.
If the closest node to this object is called A and the closest node to the end transform is called D, then it will create one point node at this object's position (call it B) and one point node at the position of the end transform (call it C), it will then connect A to B, B to C and C to D.
This link type is possible to detect while following since it has these special point nodes in the middle. The link corresponding to one of those intermediate nodes can be retrieved using the GetNodeLink method which can be of great use if you want to, for example, play a link specific animation when reaching the link.
See
The example scene RecastExample2 contains a few links which you can take a look at to see how they are used.
Public Methods
Disconnects and then reconnects the link to the graph.
Called right after all graphs have been scanned.
Public Static Methods
Public Variables
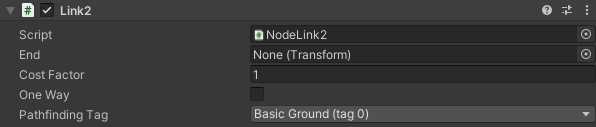
The connection will be this times harder/slower to traverse.
End position of the link.
Make a one-way connection.
The tag to apply to the link.
Inherited Public Members
Called after graphs have been updated using GraphUpdateObjects or navmesh cutting.
Called after graphs have been updated.
Called before graphs are updated using GraphUpdateObjects.
Called at the end of the scanning procedure.
Called after cached graphs have been loaded.
Called after a graph has been deserialized and loaded.
Called right before graphs are going to be scanned.
Triggers an event for all active graph modifiers.
Private/Protected Members
Removes this modifier from list of active modifiers.
Adds this modifier to list of active modifiers.
Handle serialization backwards compatibility.
Handle serialization backwards compatibility.
Unique persistent ID for this component, used for serialization.
Maps persistent IDs to the component that uses it.