Class RecastGraph Extends NavmeshBase, IUpdatableGraph
Automatically generates navmesh graphs based on world geometry.
The recast graph is based on Recast (http://code.google.com/p/recastnavigation/).
I have translated a good portion of it to C# to run it natively in Unity.
How a recast graph works
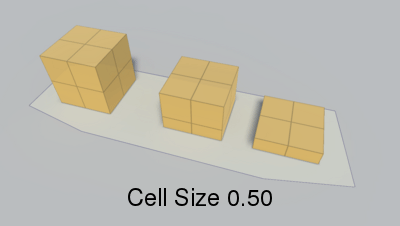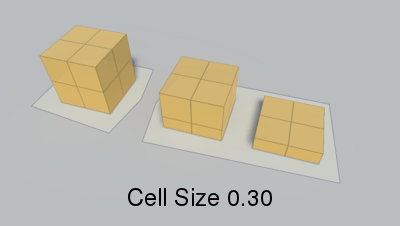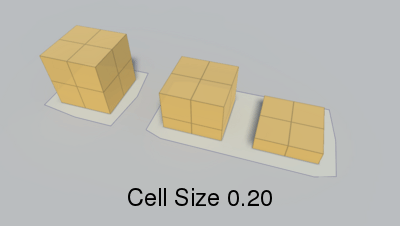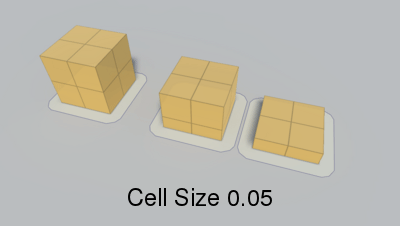
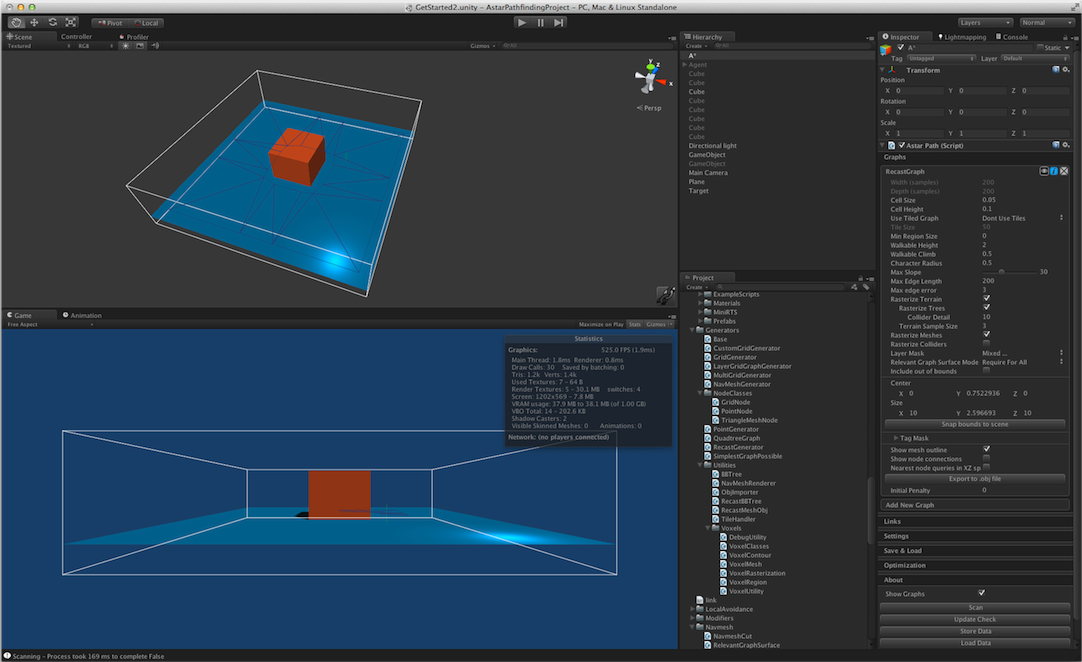
When generating a recast graph what happens is that the world is voxelized. You can think of this as constructing an approximation of the world out of lots of boxes. If you have played Minecraft it looks very similar (but with smaller boxes).
The Recast process is described as follows:
The voxel mold is build from the input triangle mesh by rasterizing the triangles into a multi-layer heightfield. Some simple filters are then applied to the mold to prune out locations where the character would not be able to move.
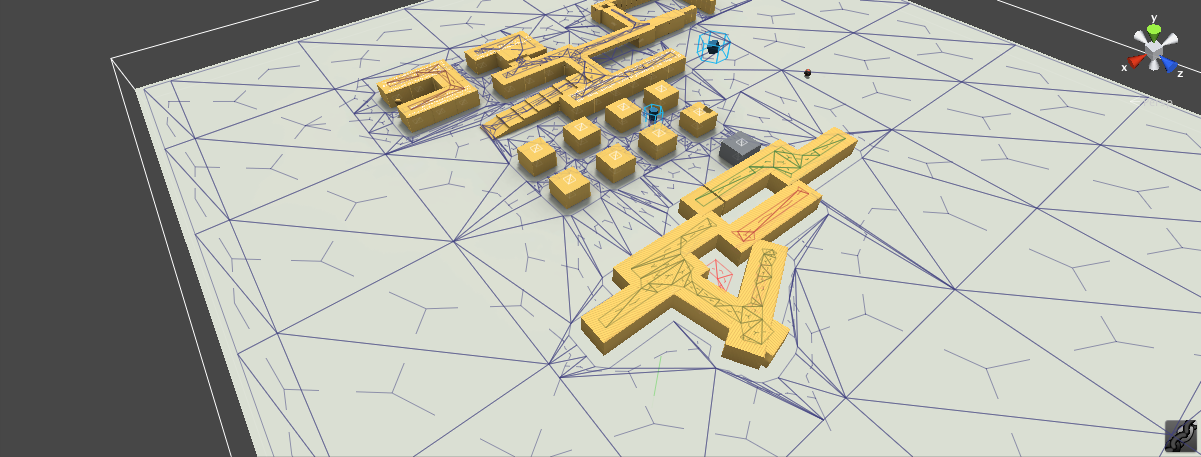
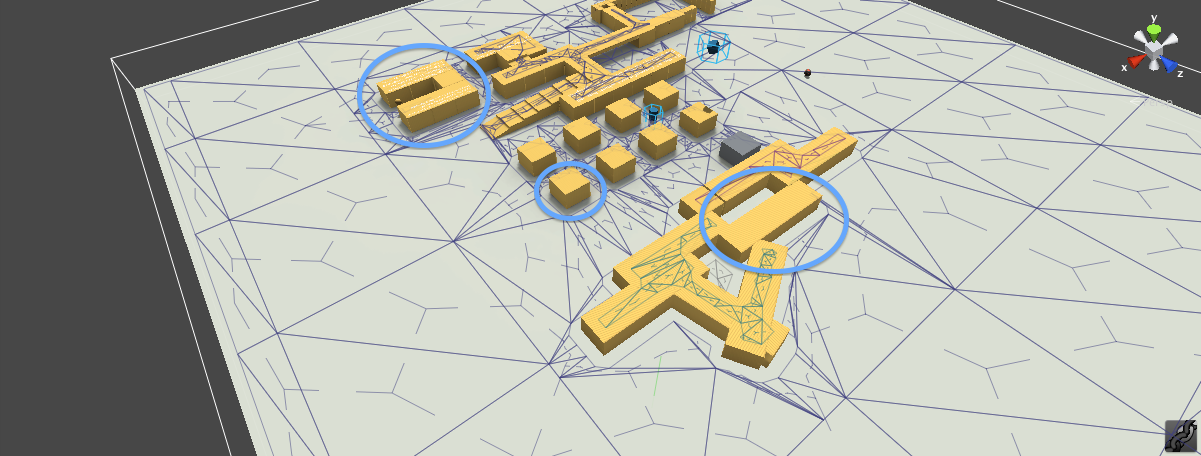
The walkable areas described by the mold are divided into simple overlayed 2D regions. The resulting regions have only one non-overlapping contour, which simplifies the final step of the process tremendously.
The navigation polygons are peeled off from the regions by first tracing the boundaries and then simplifying them. The resulting polygons are finally converted to convex polygons which makes them perfect for pathfinding and spatial reasoning about the level.
It works exactly like that in the C# version as well, except that everything is triangulated to triangles instead of n-gons. The recast generation process usually works directly on the visiable geometry in the world, this is usually a good thing, because world geometry is usually more detailed than the colliders. You can however specify that colliders should be rasterized, if you have very detailed world geometry, this can speed up the scan.
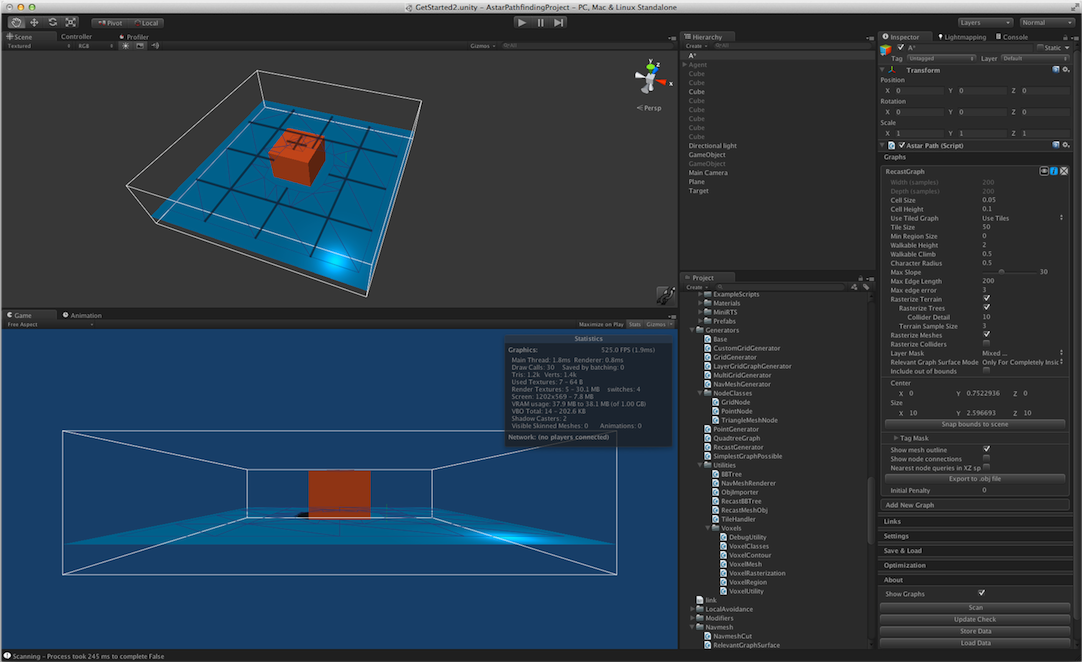
Check out the second part of the Get Started Tutorial which discusses recast graphs.
Exporting for manual editing
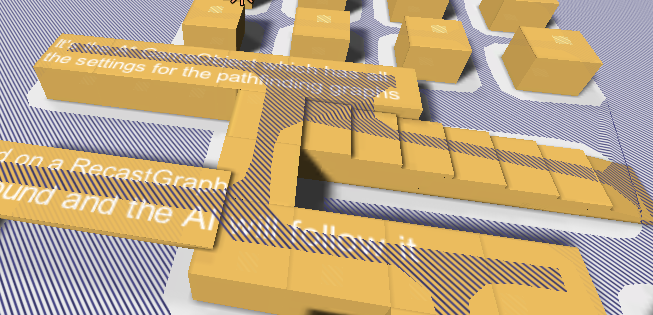
In the editor there is a button for exporting the generated graph to a .obj file. Usually the generation process is good enough for the game directly, but in some cases you might want to edit some minor details. So you can export the graph to a .obj file, open it in your favourite 3D application, edit it, and export it to a mesh which Unity can import. You can then use that mesh in a navmesh graph.
Since many 3D modelling programs use different axis systems (unity uses X=right, Y=up, Z=forward), it can be a bit tricky to get the rotation and scaling right. For blender for example, what you have to do is to first import the mesh using the .obj importer. Don't change anything related to axes in the settings. Then select the mesh, open the transform tab (usually the thin toolbar to the right of the 3D view) and set Scale -> Z to -1. If you transform it using the S (scale) hotkey, it seems to set both Z and Y to -1 for some reason. Then make the edits you need and export it as an .obj file to somewhere in the Unity project. But this time, edit the setting named "Forward" to "Z forward" (not -Z as it is per default).
A* Pro Feature:
This is an A* Pathfinding Project Pro feature only. This function/class/variable might not exist in the Free version of the A* Pathfinding Project or the functionality might be limited.
The Pro version can be bought here
Public Methods
Returns a new transform which transforms graph space to world space.
Changes the bounds of the graph to precisely encapsulate all objects in the scene that can be included in the scanning process based on the settings.
Public Variables
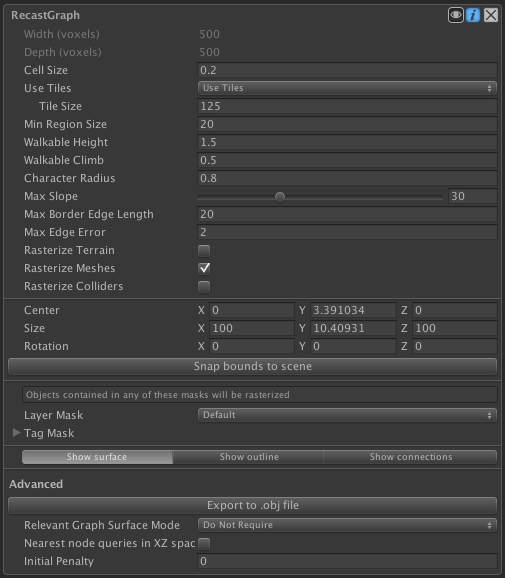
Voxel sample size (x,z).
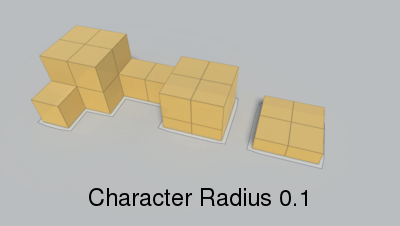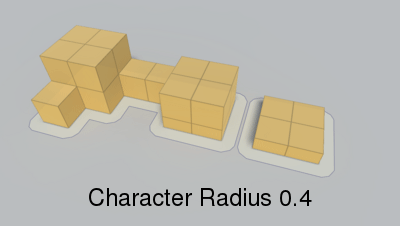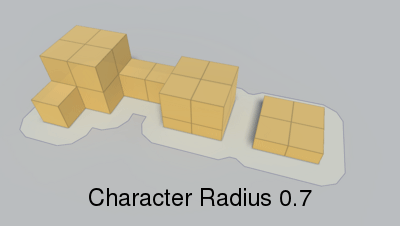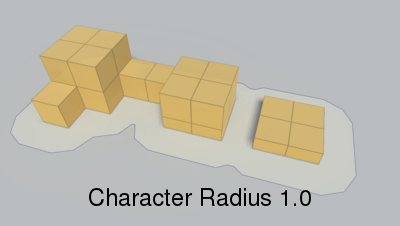
Radius of the agent which will traverse the navmesh.
Controls detail on rasterization of sphere and capsule colliders.
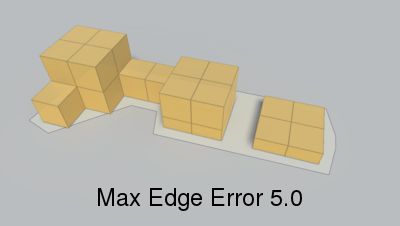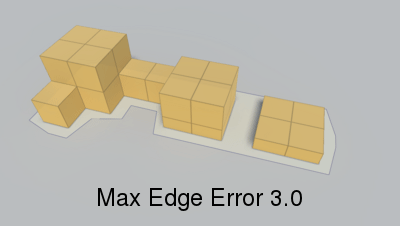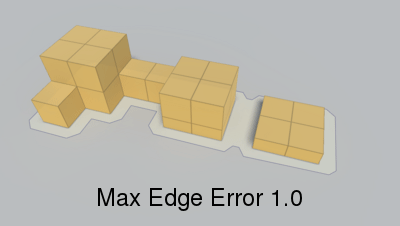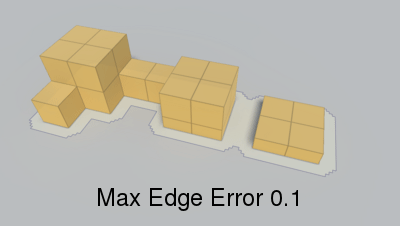
Max distance from simplified edge to real edge.
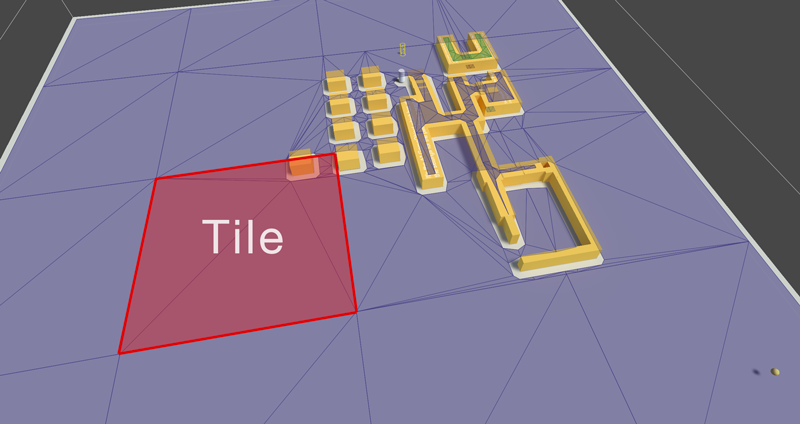
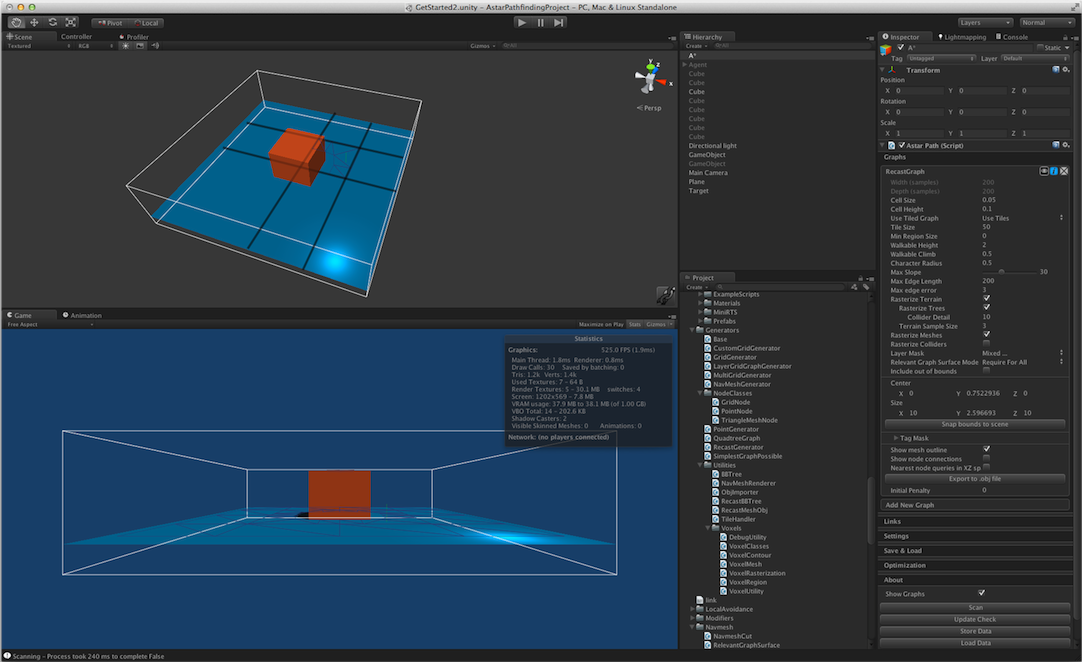
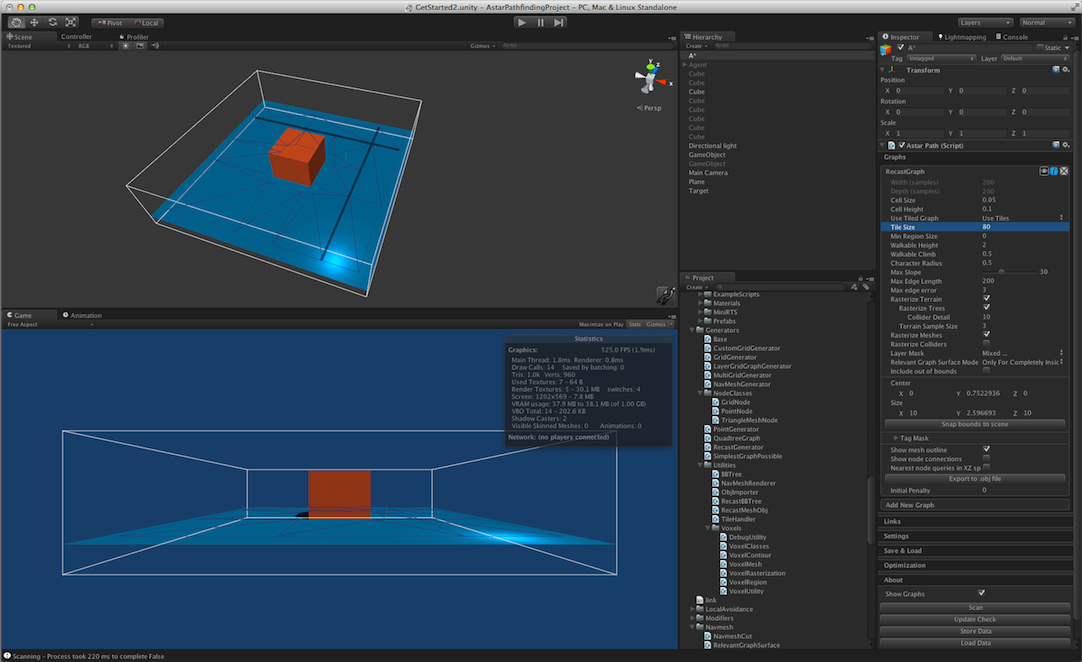
Size in voxels of a single tile.
Center of the bounding box.
Layer mask which filters which objects to include.
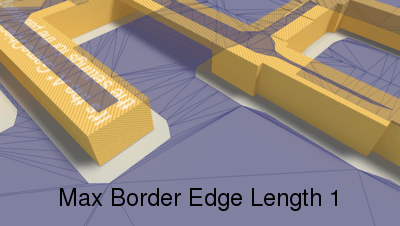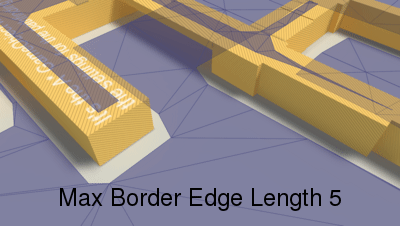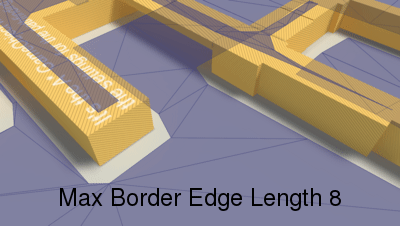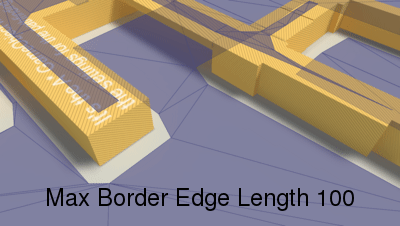
Longer edges will be subdivided.
Max slope in degrees the character can traverse.
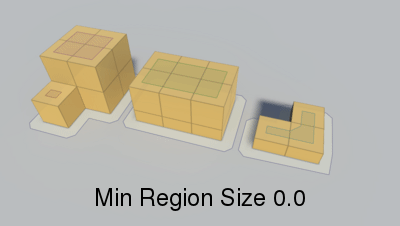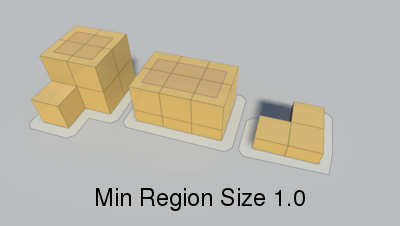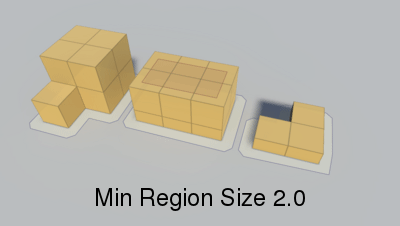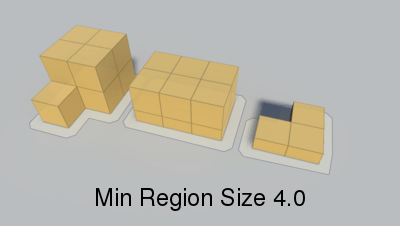
Minumum region size.
Use colliders to calculate the navmesh.
Use scene meshes to calculate the navmesh.
Include the Terrain in the scene.
Rasterize tree colliders on terrains.
Require every region to have a RelevantGraphSurface component inside it.
Rotation of the graph in degrees.
If true, scanning the graph will yield a completely empty graph.
Objects tagged with any of these tags will be rasterized.
Controls how large the sample size for the terrain is.
Size of a tile along the X axis in voxels.
Size of a tile along the Z axis in voxels.
If true, divide the graph into tiles, otherwise use a single tile covering the whole graph.
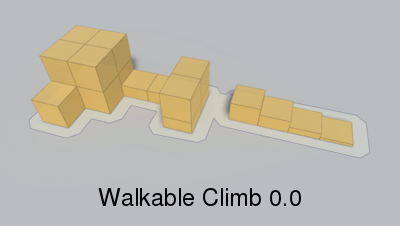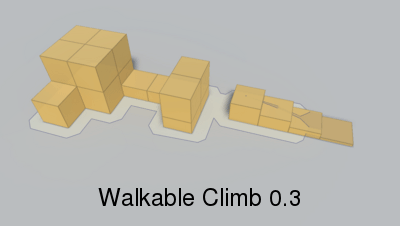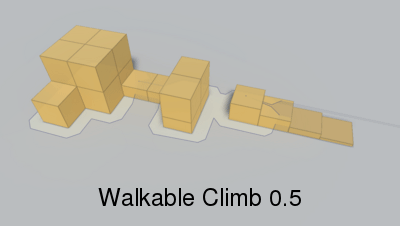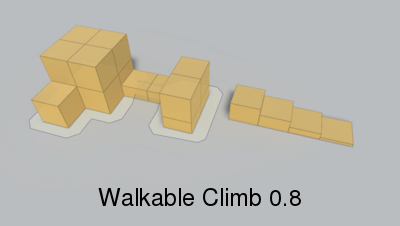
Height the character can climb.
Character height.
Public Enums
Inherited Public Members
Number of nodes in the graph.
Should navmesh cuts affect this graph.
End batch updating of tiles.
Size of the bounding box.
Returns the nearest node to a position.
Returns the nearest node to a position using the specified NNConstraint.
Returns the nearest node to a position using the specified NNConstraint.
Returns the nearest node to a position using the specified constraint .
Calls a delegate with all nodes in the graph until the delegate returns false.
Calls a delegate with all nodes in the graph.
Tile at the specified x, z coordinate pair.
Returns a bounds object with the bounding box of a group of tiles.
Returns a bounds object with the bounding box of a group of tiles.
Returns an XZ bounds object with the bounds of a group of tiles in graph space.
Returns the tile coordinate which contains the specified position.
Tile coordinates from a tile index.
Tile index from a vertex index.
All tiles.
Returns a rect containing the indices of all tiles touching the specified bounds.
Returns a rect containing the indices of all tiles touching the specified bounds.
Returns a rect containing the indices of all tiles by rounding the specified bounds to tile borders.
Vertex coordinate for the specified vertex index.
Vertex coordinate in graph space for the specified vertex index.
Index of the graph, used for identification purposes.
Used as an ID of the graph, considered to be unique.
Used in the editor to check if the info screen is open.
Default penalty to apply to all nodes.
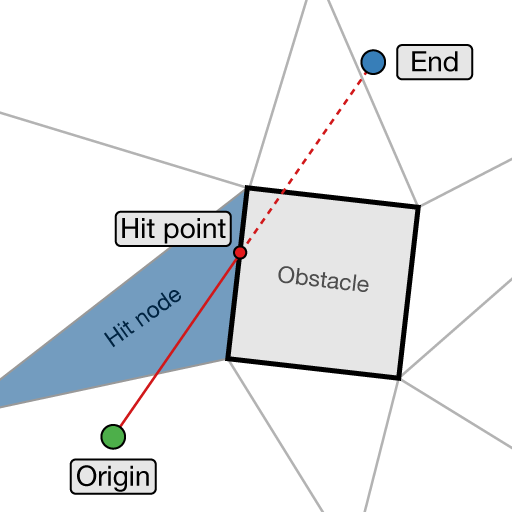
Returns if there is an obstacle between origin and end on the graph.
Returns if there is an obstacle between origin and end on the graph.
Returns if there is an obstacle between origin and end on the graph.
Returns if there is an obstacle between origin and end on the graph.
Returns if there is an obstacle between origin and end on the graph.
Returns if there is an obstacle between origin and end on the graph.
Name of the graph.
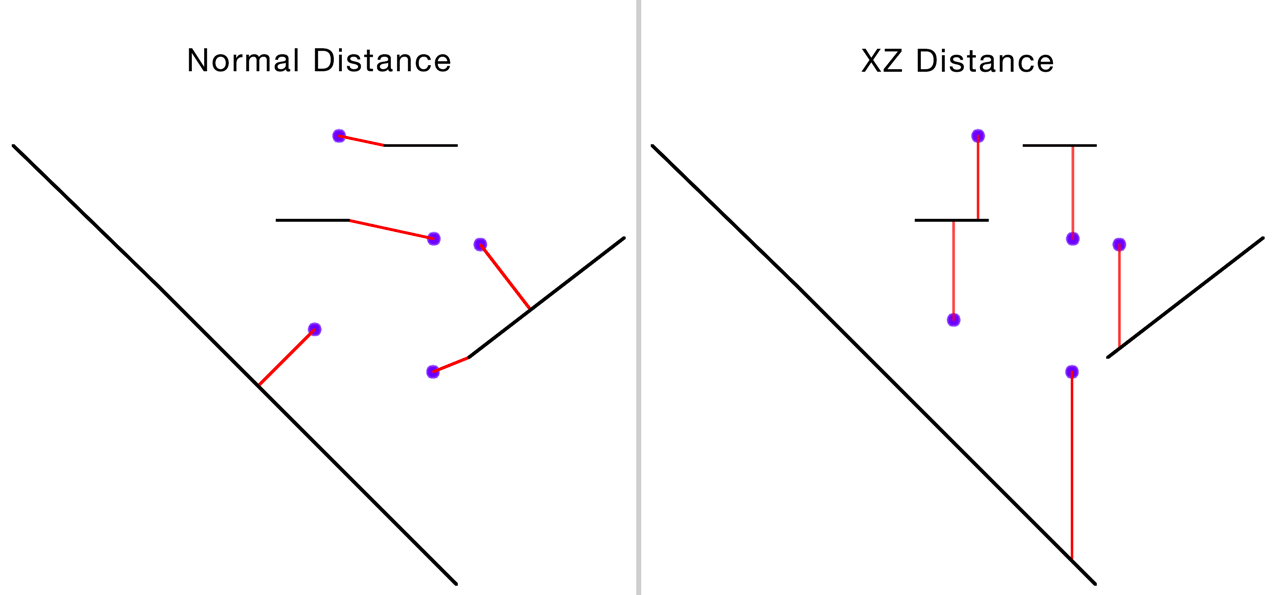
Perform nearest node searches in XZ space only.
Draw gizmos for the graph.
Called when tiles have been completely recalculated.
Is the graph open in the editor.
Finds the first node which contains position.
Moves the nodes in this graph.
Moves the nodes in this graph.
Replace tile at index with nodes created from specified navmesh.
Scan the graph.
Show the surface of the navmesh.
Start batch updating of tiles.
Number of tiles along the X-axis.
Number of tiles along the Z-axis.
Determines how the graph transforms graph space to world space.
Private/Protected Members
Convert character radius to a number of voxels.
Clear the tile at the specified coordinate.
Generate connections between the two tiles.
Create connections between all nodes.
Create a tile at tile index x, z from the mesh.
Deserializes graph type specific node data.
Destroys all nodes in the graph.
Cleans up any unmanaged data that the graph has.
True if the graph exists, false if it has been destroyed.
Fills graph with tiles created by NewEmptyTile.
Handles navmesh cutting.
Creates a single new empty tile.
Function for cleaning up references.
Called after all deserialization has been done for all graphs.
Creates a list for every tile and adds every mesh that touches a tile to the corresponding list.
Internal method to scan the graph.
Serializes Node Info.
List of tiles that have been calculated in a graph update, but have not yet been added to the graph.
Number of extra voxels on each side of a tile to ensure accurate navmeshes near the tile border.
All tiles.
Updates an area using the specified #GraphUpdateObject.
Deprecated Members
Returns the closest point of the node.
Returns if the point is inside the node in XZ space.
An old format for serializing settings.
World bounds for the graph.
Internal method to scan the graph.