Class ProceduralGraphMover Extends VersionedMonoBehaviour
Moves a grid or recast graph to follow a target.
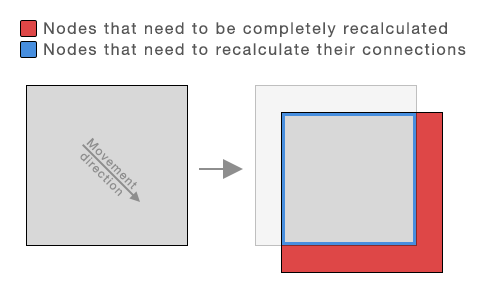
This is useful if you have a very large, or even infinite, world, but pathfinding is only necessary in a small region around an object (for example the player). This component will move a graph around so that its center stays close to the target object.
Note
This component can only be used with grid graphs, layered grid graphs and (tiled) recast graphs.
Usage
Take a look at the example scene called "Procedural" for an example of how to use this script
Attach this to some object in the scene and assign the target to e.g the player. Then the graph will follow that object around as it moves.
Performance
When the graph is moved you may notice an fps drop. If this grows too large you can try a few things:
General advice:
Turn on multithreading (A* Inspector -> Settings)
Make sure you have 'Show Graphs' disabled in the A* inspector, since gizmos in the scene view can take some time to update when the graph moves, and thus make it seem like this script is slower than it actually is.
For grid graphs:
Avoid using any erosion in the grid graph settings. This is relatively slow. Each erosion iteration requires expanding the region that is updated by 1 node.
Reduce the grid size or resolution.
Reduce the updateDistance. This will make the updates smaller but more frequent. This only works to some degree however since an update has an inherent overhead.
Disable Height Testing or Collision Testing in the grid graph if you can. This can give a performance boost since fewer calls to the physics engine need to be done.
For recast graphs:
Rasterize colliders instead of meshes. This is typically faster.
Use a reasonable tile size. Very small tiles can cause more overhead, and too large tiles might mean that you are updating too much in one go. Typical values are around 64 to 256 voxels.
Use a larger cell size. A lower cell size will give better quality graphs, but it will also be slower to scan.
For grid graphs, this script has a built-in constant called MaxMillisPerFrame and it tries to not use any more cpu time than that per frame. Recast graphs are almost entirely updated in a separate thread.
See
Public Methods
Updates the graph asynchronously.
Public Variables
Graph to update.
Index for the graph to update.
Graph will be moved to follow this target.
Grid graphs will be updated if the target is more than this number of nodes from the graph center.
True while the graph is being updated by this script.
Private/Protected Members
Approximate maximum number of milliseconds this script is allowed to use for processing each frame.
Handle serialization backwards compatibility.
Handle serialization backwards compatibility.
Update is called once per frame.
Async method for moving the grid graph.
Temporary buffer.
Temporary buffer.