|
A* Pathfinding Project
4.1.6
The A* Pathfinding Project for Unity 3D
|
|
A* Pathfinding Project
4.1.6
The A* Pathfinding Project for Unity 3D
|
Sometimes it can be necessary to update a graph during runtime. Maybe a player has constructed a new building or maybe a door has been opened. Graphs can either be completely recalculated or partially updated. A complete recalculation is good if you have changed your whole map but smaller updates can be done much faster if you have only need to change a small part of the graph.
A complete recalculation of all graphs or just a few can be done using
You can also recalculate graphs asynchronously (only available in the pro version). This does not guarantee a good frame rate, but you can at least show a loading screen.
Smaller graph updates can either be done using the GraphUpdateScene component which can be edited in the Unity inspector or using scripting which is done by calling a method in the AstarPath class with either a Bounds object or a Pathfinding.GraphUpdateObject (which is what the GraphUpdateScene component actually does in the background).
The method will then put the task in a queue to be carried out before the next path calculation. It has to be put in a queue because if it carried out directly, it might interfere with pathfinding, especially if multithreading is on, and cause all kinds of errors. This means that you might not see an update of the graph directly, but it will always be updated before the next pathfinding calculation starts (almost always, see AstarPath.limitGraphUpdates ).
Recast graphs can also be pseudo-updated using navmesh cutting. Navmesh cutting can cut out holes for obstacles in the navmesh, but cannot add more navmesh surface. See Pathfinding.NavmeshCut. This is much faster, but more limited than recalculating a whole recast tile.
Using the GraphUpdateScene component is usually easiest if you are working in the Unity Editor on a known graph. For example you can easily change the tag of a specific region without any code. However updating the graph using code is usually easier if you are doing it dynamically during runtime. For example if you are updating the graph to account for a newly placed building in a tower defence game.
When updating graphs, one usually wants to accomplish one of two things.
You might want to recalculate the graph with the same settings as it was calculated with when it was initially generated, but if you have only updated the graph in a small region, it seems wasteful to recalculate the whole graph (using AstarPath.Scan). For example the player might just have placed a new tower in a tower defence game.
Or you might want to change some settings on the existing graph. For example you might want to change the tag or penalty on some nodes.
To just recalculate a small part of the graph in the same way as it was calculated at the start can be done for all graphs except the NavMeshGraph since it usually only make sense to completely recalculate it. The way you do this using both scripting and the GraphUpdateScene component is that you set the field called "updatePhysics" to true. It might not be the most descriptive name, sorry about that.
Grid graphs will work as you expect, you can just specify the bounds and it will do everything for you. It may however recalculate a region which is slightly larger than the one you specified in order to make sure things like erosion are correctly taken into account.
Recast graphs can only be recalculated a whole tile at a time. So when a request is made to update it, all tiles which the bounds touches will be completely recalculated. Therefore it can be good to use a smaller tile size to avoid very large recalculation times. However not too small since then it essentially degenerates into a grid graph. If you use multithreading a large part of the tile recalculation will however be offloaded to a separate thread to avoid impacting the FPS too much.
Point graphs will recalculate all connections that passes through the bounds. It will however not look for new nodes that are added as GameObjects. For that you need to use AstarPath.Scan.
If you want to change properties on the exiting graph there are a bunch of things you can change.
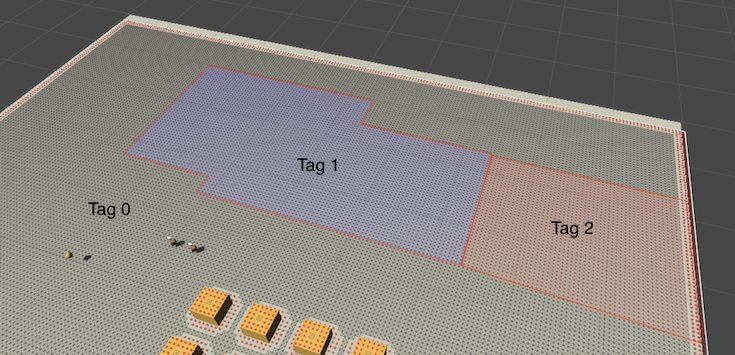
You can change the tags on the nodes. This can be used to enable some units to traverse a region while preventing other units from doing that. You can read more about tagging here: Working with tags.
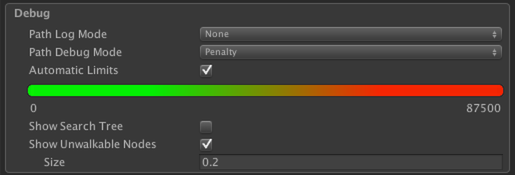
You can change the penalty on the nodes. This is used to make some nodes harder/slower to traverse compared the other nodes so that an agent will prefer some paths before others. There are some limitations though. You cannot specify negative penalties since the algorithms used cannot handle that (and if they could, the system would be a lot slower). However a common trick is to set a very large initial penalty (which can be done in the graph settings) and then decrease the penalty from that high value. Note however that this will make pathfinding slower overall since it has to search more nodes. The penalty values that are required are quite high. There is no real "penalty unit" however a penalty of 1000 corresponds roughly to one world unit of travel.
Walkability of the nodes can also be modified directly. So you can make all nodes within some bounds be all walkable or all unwalkable.
For information about how to use the GraphUpdateScene component . See the docs for that class. The GraphUpdateScene component settings map almost 1 to 1 to the GraphUpdateObject which is used when updating graphs using scripting. So I recommend that you read that page even though you are only going to use scripting.
To update a graph you create a GraphUpdateObject and set the parameters you want, then you call the AstarPath.UpdateGraphs method to queue the update.
The bounds variable referred to is a UnityEngine.Bounds object. It defines an axis aligned box in which to update the graphs in. Often you want to update the graph around some newly created object. In the example the bounding box is taken from the attached collider.
However make sure that this object will be recognised by the graph. For grid graphs you should make sure that the object's layer is included in either the collision testing mask or the height teting mask.
If you don't need to recalculate all parameters on the nodes when using a grid graph or connections when using a point graph, you can set updatePhysics (see GridGraph specific details) to false to avoid unnecessary calculations
For details about exactly what fields to set, take a look at the class documentation for the GraphUpdateObject .
In some cases it might be inconvenient to use a GraphUpdateObject to update the graph. In those cases you can update the graph data directly. However care needs to be taken. When using the GraphUpdateObject the system takes care of a lot of things for you.
Graph data must only be modified when it is safe to do so. Pathfinding might be running at any time so it is necessary to first pause the pathfinding threads and then update the data. The easiest way to do this is to use AstarPath.AddWorkItem:
Some care needs to be taken to make sure that the pathfinding data is up to date after you have changed it. If you have changed the walkability or connections of any node, you need to update the 'area' information (which is visualized as different colors if you have set A* Inspector -> Settings -> Graph Coloring to "Areas"). This is used by the system to determine which nodes are reachable from which other nodes which is in turn used to quickly determine if a path is possible or not.
The flood fill calls are batched for performance so that multiple graph updates which are executed directly after each other do not have to run the flood fill more than once. If your work item requires that the area information is up to date you should call the ctx.EnsureValidFloodFill method first. Usually this is not something that work items require however.
If you are modifying walkability you also need to make sure that connections are recalculated properly. This is important mostly for the grid graph. You can use the GridGraph.CalculateConnections method. Note that this needs to be called both on the node you changed walkability on and also the nodes adjacent to it since they might have to change their connections to add or remove that node as a connection.
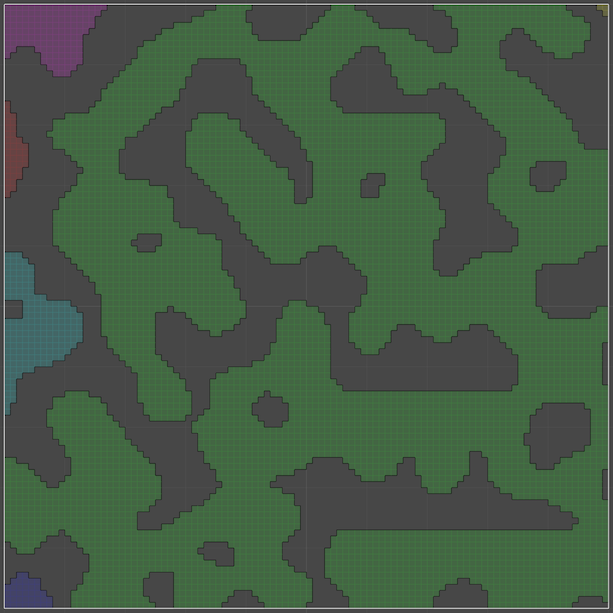
Here is an example of changing all nodes in a grid graph and using perlin noise to determine if nodes should be walkable:
The above code will generate this graph:

The AddWorkItem method can also be used in more advanced ways. For example it allows you to spread the calculation over multiple frames if necessary:
For a list of all different ways of creating a work item, take a look at the constructors for Pathfinding.AstarWorkItem.
While some things like walkability and position are immediately visible changes. Tags and penalties are not directly visible on the graph. However there are other viewing modes that can be enabled to visualize both tags and penalties.
The viewing mode can be edited at A* Inspector -> Settings -> Debug -> Graph Coloring. If you set it to "Tags" all tags will be visible as different colors on the graph.
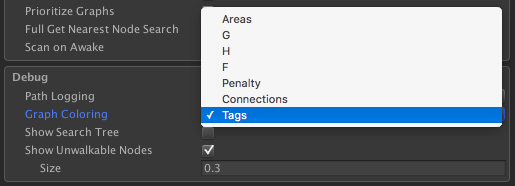
You can also set it to show penalties. By default it will automatically adjust itself so that the node(s) with the highest penalty will show up as pure red and the node(s) with the lowest penalty will show up as green.
When updating is carried out using a GraphUpdateObject, all graphs will be looped over and those which can be updated (all built in ones) will have their UpdateArea function called (i.e be updated).
Each node is updated by the graphs calling Pathfinding.GraphUpdateObject.Apply sending each affected node to it, the Apply function will then change penalty, walkability or other parameters specified. Graphs can also use custom updating logic, such as the GridGraph (see GridGraph specific details). You do not have to understand all different function calls to be able to use it, those are mostly for people who want to mess around with the source code.
The updatePhysics variable matters a lot when updating grid graphs. If it is set to true, all nodes affected will have their height recalculated and then checked if they are still walkable. You usually want to leave this to true when updating a grid graph.
When updating a GridGraph, the GraphUpdateObject's Apply function (which changed walkability, tags and penalties) will be called for each node inside the bounds, it will check the updatePhysics variable, if it is true (which is the default value), the area will be expanded by the diameter of the specified in the Collision Testing settings and every node inside the area will be checked for collisions. If it is false, however, only the Apply function will be called for the nodes inside the area (not expanded) and nothing else will be done.
Navmesh based graphs (NavMeshGraph and RecastGraph) only have support for updating penalty, walkability and similar on already existing nodes or for recast graphs, to completely recalculate whole tiles. New nodes cannot be created using GraphUpdateObjects (unless recalculating whole tiles). The GraphUpdateObject will affect all nodes/triangles which intersect or are contained by the GUO's bounds.
For recast graphs you can also use navmesh cutting to update the graph in a fast way.
Point graphs will call Apply on every node inside the bounds. If GraphUpdateObject.updatePhysics is set to true (default true) it will also recalculate all connections which passes through the bounds object.
The GraphUpdateObject contains some basic variables on how to update each node. See documentation for the Pathfinding.GraphUpdateObject for more info.
Classes can inherit from the GraphUpdateObject to override some functionality.
Here's an example of a GraphUpdateObject which moves nodes by some offset while still keeping the base functionality.
You could then use that GUO like this:
A common thing in tower defence games is to make sure that the towers the player places does not block the path between the spawn points and the goal. This might seem hard to do, but luckily there is an API for that.
The Pathfinding.GraphUpdateUtilities.UpdateGraphsNoBlock method can be used to first check if a given graph update object will cause the path between two or more points to become blocked. This is however slower than a normal graph update so you probably don't want to use it too often.
For example when a player in a tower defence game places a tower, you could instantiate it, then call the UpdateGraphsNoBlock method to check if the newly placed tower will block the path. If it did then remove the tower immediately and notify the player that the choosen position was not valid. You can pass a list of nodes to the UpdateGraphsNoBlock method so you could for example make sure that not only is the path from the start to the goal not blocked, but also that all units can still reach the goal (if it is possible to place towers when enemies are walking around).