float
centerOffset = 1
Offset along the Y coordinate for the ground raycast start position.
Normally the pivot of the character is at the character's feet, but you usually want to fire the raycast from the character's center, so this value should be half of the character's height.
A green gizmo line will be drawn upwards from the pivot point of the character to indicate where the raycast will start.
Position in the world that this agent should move to.
If no destination has been set yet, then (+infinity, +infinity, +infinity) will be returned.
Note that setting this property does not immediately cause the agent to recalculate its path. So it may take some time before the agent starts to move towards this point. Most movement scripts have a repathRate field which indicates how often the agent looks for a new path. You can also call the SearchPath method to immediately start to search for a new path. Paths are calculated asynchronously so when an agent starts to search for path it may take a few frames (usually 1 or 2) until the result is available. During this time the pathPending property will return true.
If you are setting a destination and then want to know when the agent has reached that destination then you should check both pathPending and reachedEndOfPath: IEnumerator Start () {
ai.destination = somePoint;
// Start to search for a path to the destination immediately
// Note that the result may not become available until after a few frames
// ai.pathPending will be true while the path is being calculated
ai.SearchPath();
// Wait until we know for sure that the agent has calculated a path to the destination we set above
while (ai.pathPending || !ai.reachedEndOfPath) {
yield return null;
}
// The agent has reached the destination now
}
void
FinalizeMovement
(
Vector3 | nextPosition | New position of the agent. |
Quaternion | nextRotation | New rotation of the agent. If enableRotation is false then this parameter will be ignored. |
)
Moves the agent to a position.
This is used if you want to override how the agent moves. For example if you are using root motion with Mecanim.
This will use a CharacterController, Rigidbody, Rigidbody2D or the Transform component depending on what options are available.
The agent will be clamped to the navmesh after the movement (if such information is available, generally this is only done by the RichAI component).
bool
funnelSimplification = false
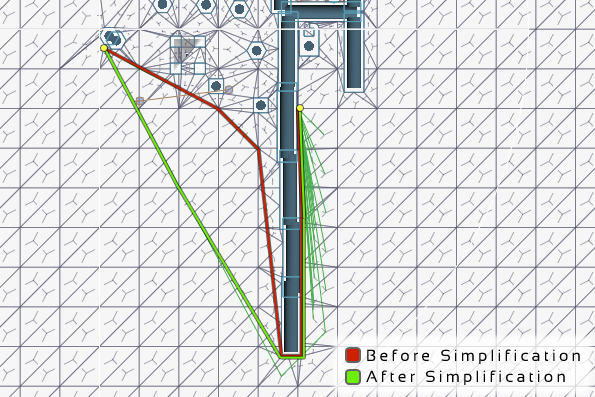
Use funnel simplification.
On tiled navmesh maps, but sometimes on normal ones as well, it can be good to simplify the funnel as a post-processing step to make the paths straighter.
This has a moderate performance impact during frames when a path calculation is completed.
The RichAI script uses its own internal funnel algorithm, so you never need to attach the FunnelModifier component.
bool
isStopped
Gets or sets if the agent should stop moving.
If this is set to true the agent will immediately start to slow down as quickly as it can to come to a full stop. The agent will still react to local avoidance and gravity (if applicable), but it will not try to move in any particular direction.
The current path of the agent will not be cleared, so when this is set to false again the agent will continue moving along the previous path.
This is a purely user-controlled parameter, so for example it is not set automatically when the agent stops moving because it has reached the target. Use reachedEndOfPath for that.
If this property is set to true while the agent is traversing an off-mesh link (RichAI script only), then the agent will continue traversing the link and stop once it has completed it.
Note
This is not the same as the canMove setting which some movement scripts have. The canMove setting disables movement calculations completely (which among other things makes it not be affected by local avoidance or gravity). For the AILerp movement script which doesn't use gravity or local avoidance anyway changing this property is very similar to changing canMove.
The steeringTarget property will continue to indicate the point which the agent would move towards if it would not be stopped.
void
Move
(
Vector3 | deltaPosition | Direction and distance to move the agent in world space. |
)
Move the agent.
This is intended for external movement forces such as those applied by wind, conveyor belts, knockbacks etc.
Some movement scripts may ignore this completely (notably the AILerp script) if it does not have any concept of being moved externally.
The agent will not be moved immediately when calling this method. Instead this offset will be stored and then applied the next time the agent runs its movement calculations (which is usually later this frame or the next frame). If you want to move the agent immediately then call: ai.Move(someVector);
ai.FinalizeMovement(ai.position, ai.rotation);
void
MovementUpdate
(
float | deltaTime | time to simulate movement for. Usually set to Time.deltaTime. |
out Vector3 | nextPosition | the position that the agent wants to move to during this frame. |
out Quaternion | nextRotation | the rotation that the agent wants to rotate to during this frame. |
)
Calculate how the character wants to move during this frame.
Note that this does not actually move the character. You need to call FinalizeMovement for that. This is called automatically unless canMove is false.
To handle movement yourself you can disable canMove and call this method manually. This code will replicate the normal behavior of the component: void Update () {
// Disable the AIs own movement code
ai.canMove = false;
Vector3 nextPosition;
Quaternion nextRotation;
// Calculate how the AI wants to move
ai.MovementUpdate(Time.deltaTime, out nextPosition, out nextRotation);
// Modify nextPosition and nextRotation in any way you wish
// Actually move the AI
ai.FinalizeMovement(nextPosition, nextRotation);
}
System.Func<RichSpecial, IEnumerator>
onTraverseOffMeshLink
Called when the agent starts to traverse an off-mesh link.
Register to this callback to handle off-mesh links in a custom way.
If this event is set to null then the agent will fall back to traversing off-mesh links using a very simple linear interpolation.
void OnEnable () {
ai = GetComponent<RichAI>();
if (ai != null) ai.onTraverseOffMeshLink += TraverseOffMeshLink;
}
void OnDisable () {
if (ai != null) ai.onTraverseOffMeshLink -= TraverseOffMeshLink;
}
IEnumerator TraverseOffMeshLink (RichSpecial link) {
// Traverse the link over 1 second
float startTime = Time.time;
while (Time.time < startTime + 1) {
transform.position = Vector3.Lerp(link.first.position, link.second.position, Time.time - startTime);
yield return null;
}
transform.position = link.second.position;
}
OrientationMode
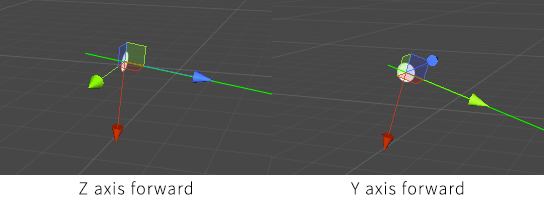
orientation = OrientationMode.ZAxisForward
Determines which direction the agent moves in.
For 3D games you most likely want the ZAxisIsForward option as that is the convention for 3D games. For 2D games you most likely want the YAxisIsForward option as that is the convention for 2D games.
Using the YAxisForward option will also allow the agent to assume that the movement will happen in the 2D (XY) plane instead of the XZ plane if it does not know. This is important only for the point graph which does not have a well defined up direction. The other built-in graphs (e.g the grid graph) will all tell the agent which movement plane it is supposed to use.
bool
reachedEndOfPath
True if the agent has reached the end of the current path.
This is the approximate distance the AI has to move to reach the end of the path it is currently traversing.
Note that setting the destination does not immediately update the path, nor is there any guarantee that the AI will actually be able to reach the destination that you set. The AI will try to get as close as possible.
It is very hard to provide a method for detecting if the AI has reached the destination that works across all different games because the destination may not even lie on the navmesh and how that is handled differs from game to game (see also the code snippet in the docs for destination).
float
remainingDistance
Remaining distance along the current path to the end of the path.
For the RichAI movement script this may not always be precisely known, especially when far away from the destination. In those cases an approximate distance will be returned.
If the agent does not currently have a path, then positive infinity will be returned.
void
SearchPath
()
Recalculate the current path.
You can for example use this if you want very quick reaction times when you have changed the destination so that the agent does not have to wait until the next automatic path recalculation (see canSearch).
If there is an ongoing path calculation, it will be canceled, so make sure you leave time for the paths to get calculated before calling this function again. A canceled path will show up in the log with the message "Canceled by script" (see #Seeker.CancelCurrentPathRequest()).
If no destination has been set yet then nothing will be done.
Note
The path result may not become available until after a few frames. During the calculation time the pathPending property will return true.
void
SetPath
(
)
Make the AI follow the specified path.
In case the path has not been calculated, the script will call seeker.StartPath to calculate it. This means the AI may not actually start to follow the path until in a few frames when the path has been calculated. The pathPending field will as usual return true while the path is being calculated.
In case the path has already been calculated it will immediately replace the current path the AI is following. This is useful if you want to replace how the AI calculates its paths. Note that if you calculate the path using seeker.StartPath then this script will already pick it up because it is listening for all paths that the Seeker finishes calculating. In that case you do not need to call this function.
You can disable the automatic path recalculation by setting the canSearch field to false.
// Disable the automatic path recalculation
ai.canSearch = false;
var pointToAvoid = enemy.position;
// Make the AI flee from the enemy.
// The path will be about 20 world units long (the default cost of moving 1 world unit is 1000).
var path = FleePath.Construct(ai.position, pointToAvoid, 1000 * 20);
ai.SetPath(path);
void
Teleport
(
Vector3 | newPosition | |
bool | clearPath=true | |
)
Instantly move the agent to a new position.
This will trigger a path recalculation (if clearPath is true, which is the default) so if you want to teleport the agent and change its destination it is recommended that you set the destination before calling this method.
The current path will be cleared by default.
See
Works similarly to Unity's NavmeshAgent.Warp.
SearchPath
When setting transform.position directly the agent will be clamped to the part of the navmesh it can reach, so it may not end up where you wanted it to. This ensures that the agent can move to any part of the navmesh.